The documentation you are viewing is for Dapr v1.7 which is an older version of Dapr. For up-to-date documentation, see the latest version.
Publish and subscribe overview
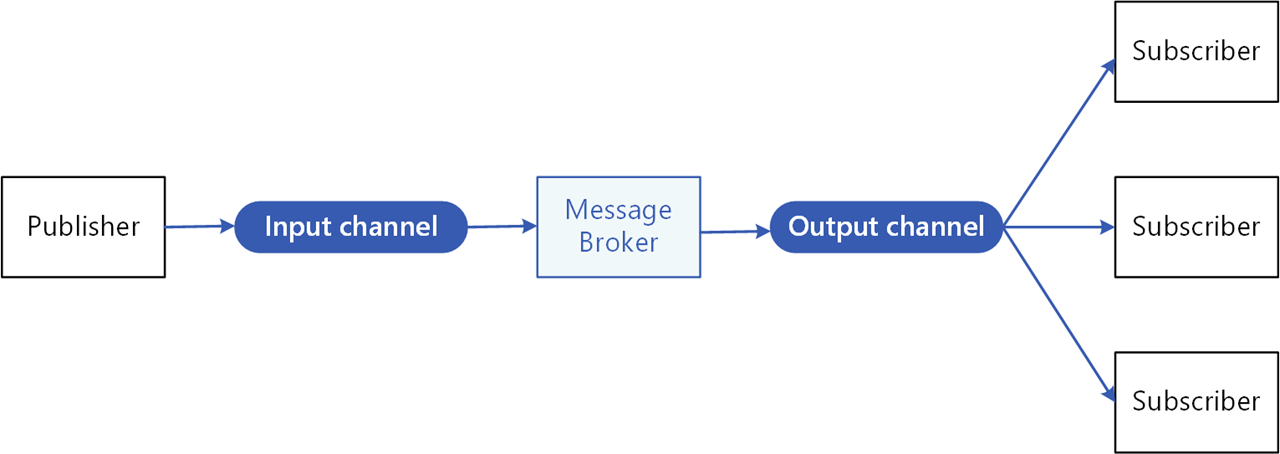
Publish and subscribe pattern
The publish and subscribe pattern (pub/sub) enables microservices to communicate with each other using messages for event-driven architectures.
- The producer, or publisher, writes messages to an input channel and sends them to a topic, unaware which application will receive them.
- The consumer, or subscriber, subscribes to the topic and receives messages from an output channel, unaware which service produced these messages.
An intermediary message broker copies each message from a publisher’s input channel to an output channel for all subscribers interested in that message. This pattern is especially useful when you need to decouple microservices from one another.
Pub/sub API in Dapr
The pub/sub API in Dapr:
- Provides a platform-agnostic API to send and receive messages.
- Offers at-least-once message delivery guarantee.
- Integrates with various message brokers and queuing systems.
The specific message broker used by your service is pluggable and configured as a Dapr pub/sub component at runtime. This removes the dependency from your service and makes your service more portable and flexible to changes.
When using pub/sub in Dapr:
- Your service makes a network call to a Dapr pub/sub building block API.
- The pub/sub building block makes calls into a Dapr pub/sub component that encapsulates a specific message broker.
- To receive messages on a topic, Dapr subscribes to the pub/sub component on behalf of your service with a topic and delivers the messages to an endpoint on your service when they arrive.
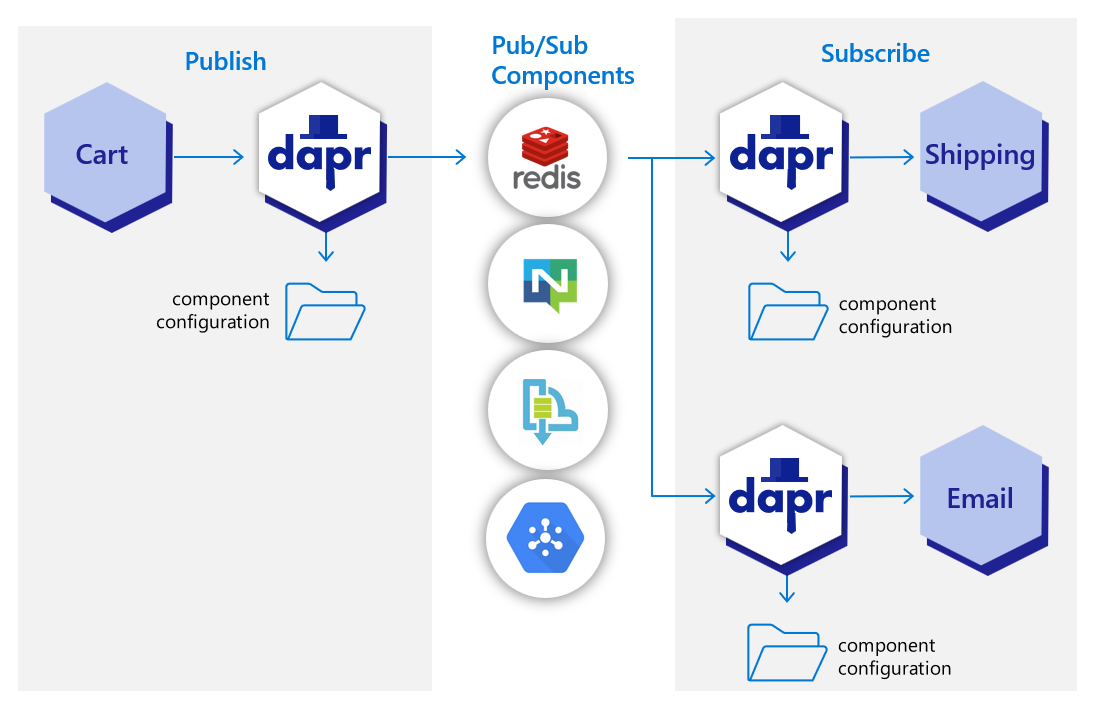
In the diagram below, a “shipping” service and an “email” service have both subscribed to topics published by a “cart” service. Each service loads pub/sub component configuration files that point to the same pub/sub message bus component; for example: Redis Streams, NATS Streaming, Azure Service Bus, or GCP pub/sub.
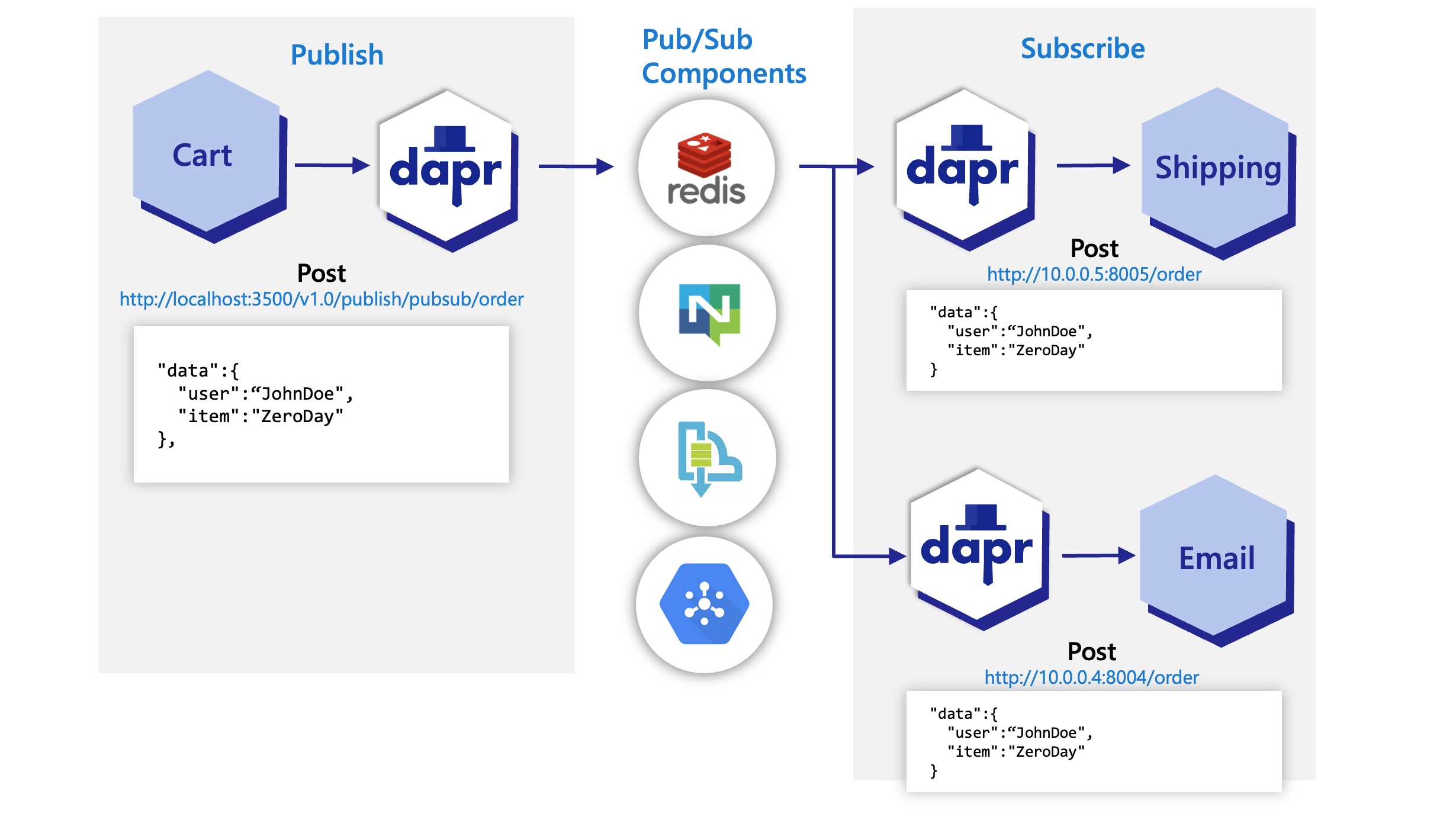
In the diagram below, the Dapr API posts an “order” topic from the publishing “cart” service to “order” endpoints on the “shipping” and “email” subscribing services.
View the complete list of pub/sub components that Dapr supports.
Dapr pub/sub API features
The pub/sub building block brings several features to your application.
Sending messages using Cloud Events
To enable message routing and provide additional context with each message between services, Dapr uses the CloudEvents 1.0 specification as its message format. Any message sent by an application to a topic using Dapr is automatically wrapped in a Cloud Events envelope, using Content-Type header value for datacontenttype attribute.
For more information, read about messaging with CloudEvents, or sending raw messages without CloudEvents.
Communication with applications not using Dapr and CloudEvents
If one of your applications uses Dapr while another doesn’t, you can disable the CloudEvent wrapping for a publisher or subscriber. This allows partial adoption of Dapr pub/sub in applications that cannot adopt Dapr all at once.
For more information, read how to use pub/sub without CloudEvents.
Setting message content types
When publishing a message, it’s important to specify the content type of the data being sent. Unless specified, Dapr will assume text/plain.
- HTTP client: the content type can be set in a
Content-Typeheader - gRPC client and SDK: have a dedicated content type parameter
Message delivery
In principle, Dapr considers a message successfully delivered once the subscriber processes the message and responds with a non-error response. For more granular control, Dapr’s pub/sub API also provides explicit statuses, defined in the response payload, with which the subscriber indicates specific handling instructions to Dapr (for example, RETRY or DROP).
Receiving messages with topic subscriptions
Dapr applications can subscribe to published topics via two methods that support the same features: declarative and programmatic.
| Subscription method | Description |
|---|---|
| Declarative | Subscription is defined in an external file. The declarative approach removes the Dapr dependency from your code and allows for existing applications to subscribe to topics, without having to change code. |
| Programmatic | Subscription is defined in the user code. The programmatic approach implements the subscription in your code. |
For more information, read about the subscriptions in Subscription Methods.
Message routing
Dapr provides content-based routing pattern. Pub/sub routing is an implementation of this pattern that allows developers to use expressions to route CloudEvents based on their contents to different URIs/paths and event handlers in your application. If no route matches, an optional default route is used. This is useful as your applications expands to support multiple event versions or special cases.
This feature is available to both the declarative and programmatic subscription approaches.
For more information on message routing, read Dapr pub/sub API reference
At-least-once guarantee
Dapr guarantees at-least-once semantics for message delivery. When an application publishes a message to a topic using the pub/sub API, Dapr ensures the message is delivered at least once to every subscriber.
Consumer groups and competing consumers pattern
Dapr automatically handles the burden of dealing with concepts like consumer groups and competing consumers pattern. The competing consumers pattern refers to multiple application instances using a single consumer group. When multiple instances of the same application (running same Dapr app ID) subscribe to a topic, Dapr delivers each message to only one instance of that application. This concept is illustrated in the diagram below.
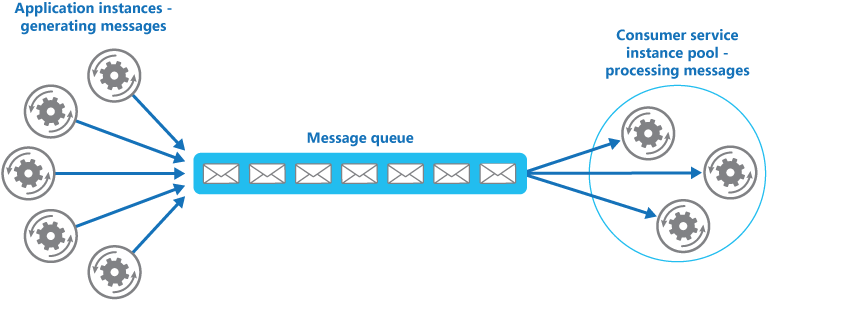
Similarly, if two different applications (with different app-IDs) subscribe to the same topic, Dapr delivers each message to only one instance of each application.
Scoping topics for added security
By default, all topic messages associated with an instance of a pub/sub component are available to every application configured with that component. You can limit which application can publish or subscribe to topics with Dapr topic scoping. For more information, read: pub/sub topic scoping.
Message Time-to-Live (TTL)
Dapr can set a timeout message on a per-message basis, meaning that if the message is not read from the pub/sub component, then the message is discarded. This timeout message prevents a build up of unread messages. If a message has been in the queue longer than the configured TTL, it is marked as dead. For more information, read pub/sub message TTL.
Try out pub/sub
Quickstarts and tutorials
Want to put the Dapr pub/sub API to the test? Walk through the following quickstart and tutorials to see pub/sub in action:
| Quickstart/tutorial | Description |
|---|---|
| Pub/sub quickstart | Send and receive messages using the publish and subscribe API. |
| Pub/sub tutorial | Demonstrates how to use Dapr to enable pub-sub applications. Uses Redis as a pub-sub component. |
Start using pub/sub directly in your app
Want to skip the quickstarts? Not a problem. You can try out the pub/sub building block directly in your application to publish messages and subscribe to a topic. After Dapr is installed, you can begin using the pub/sub API starting with the pub/sub how-to guide.
Next steps
- Learn about messaging with CloudEvents and when you might want to send messages without CloudEvents.
- Follow How-To: Configure pub/sub components with multiple namespaces.
- Review the list of pub/sub components.
- Read the API reference.
Feedback
Was this page helpful?
Glad to hear it! Please tell us how we can improve.
Sorry to hear that. Please tell us how we can improve.